 YouGov’s international study conducted in 23 countries and regions captures the sentiments of people and the differing attitude to the disease
YouGov’s international study conducted in 23 countries and regions captures the sentiments of people and the differing attitude to the disease
The Coronavirus has become a subject of discussion worldwide ever since it was first detected in 2019. Having started in Wuhan province in China, the disease has since spread to more than 35 countries outside China, claiming more than 2700 lives globally, as per WHO reports.
YouGov’s international study conducted among more than 27,000 people in 23 countries and regions captures the sentiments of people and the differing attitude to the disease. Even though the coronavirus outbreak has been the most significant international news story for the past two months, familiarity with the disease is not evenly spread.
Generally speaking, people in Europe and the US report lower levels of familiarity with the ailment as compared to those from the GCC region. Awareness within the Asia-Pacific region- which is the most heavily afflicted- seems to be varied.
Respondents in the Philippines seem especially aware of the virus, with 68% saying they are “very familiar” with it and a further 28% feeling “somewhat familiar”.
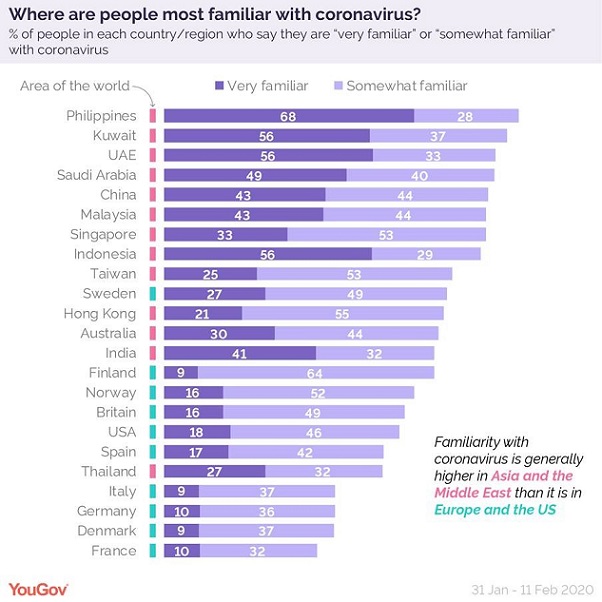
At the opposite end of the spectrum is Thailand, where only 27% report being very familiar with the disease, and a further 32% somewhat familiar.
In China, the source of the outbreak, 43% say they are very familiar and a further 44% somewhat familiar. In nearby Hong Kong and Singapore, however, only 21% and 33% respectively, feel very familiar and between 53% and 55% somewhat familiar.
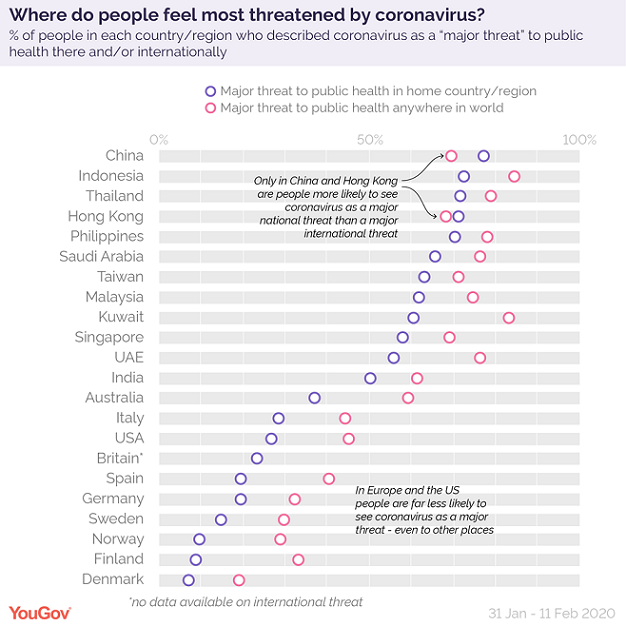
The threat of the virus has become a global concern. Unsurprisingly people in China are most likely to think that coronavirus is a threat to public health in their own country.
People in Asian and GCC nations are substantially more likely to feel threatened by the disease than Europeans and Americans. In Asia-Pacific and the GCC region the majority (58% to 77%) consider the virus a major threat (with Australia an exception at 37%). In the nine European countries surveyed this figure ranges only from 7% to 28%, while in the USA it stands at 27%.
In addition, in almost every country and region surveyed people are more likely to see coronavirus as a major threat globally than at home, with the exception of two places where this is not the case: China and Hong Kong. The 69% of Chinese people who see the disease as a major threat anywhere in the world is eight points lower than the 77% who see it as a major threat nationally. In Hong Kong the difference is between 71% and 68%.
Looking specifically at the GCC region, we see that the majority (89%) of residents from the three surveyed countries in the region- UAE, KSA and Kuwait, are familiar with Corona virus, and six in ten (59%) consider it to be a major threat to public health in their country. Respondents from Saudi Arabia (67%) are more likely to consider corona virus as a major threat in their area of residence, followed by people in Kuwait (61%) and UAE (52%).
Recently, the World Health Organisation listed some recommendations for people to protect themselves and others from getting infected. Overall, fewer than two-thirds of GCC residents are already taking these precautionary measures to safeguards themselves against the disease. 65% maintain personal hygiene by washing their hands regularly, and almost as many (61%) maintain social distance by refraining from visiting crowded areas. Many avoid close contact with people who are sick (58%), cover their nose and mouth while coughing (52%). Comparatively, fewer people avoid touching eyes, nose or mouth with unwashed hands (46%) although it is one of the top recommendations by the health authorities.


